Overview
This project analyzes images from the IAM Handwriting Dataset for two objectives at once: transcribing the written words/sentences and identifying who wrote them. CNN, CRNN, SVM, Siamese Networks, and XGBoost configurations all run through the same experimental pipeline, creating a reproducible blueprint for biometric verification, forensic analysis, and intelligent document workflows.
Project Motivation
Conventional handwriting systems only learn what was written. Here the pipeline also models who wrote it by capturing cues like stroke pressure, spacing, slant, and rhythm. Recognition and verification models share the same data path so even with few samples, the system can still attribute authorship.
Dataset & Preprocessing
- Selected the 49 IAM writers with the most samples, yielding 4,207 single-channel 113×113 images.
- Applied margin cropping, grayscale normalization, and augmentation (rotation, inversion, noise) to enrich data.
- One-hot encoded writer labels and used stratified train/validation/test splits to keep classes balanced.


The verification problem changes difficulty depending on how distinctive the handwriting is. I therefore curated two qualitative buckets that were used for human-in-the-loop checks:


Model Architectures
CNN
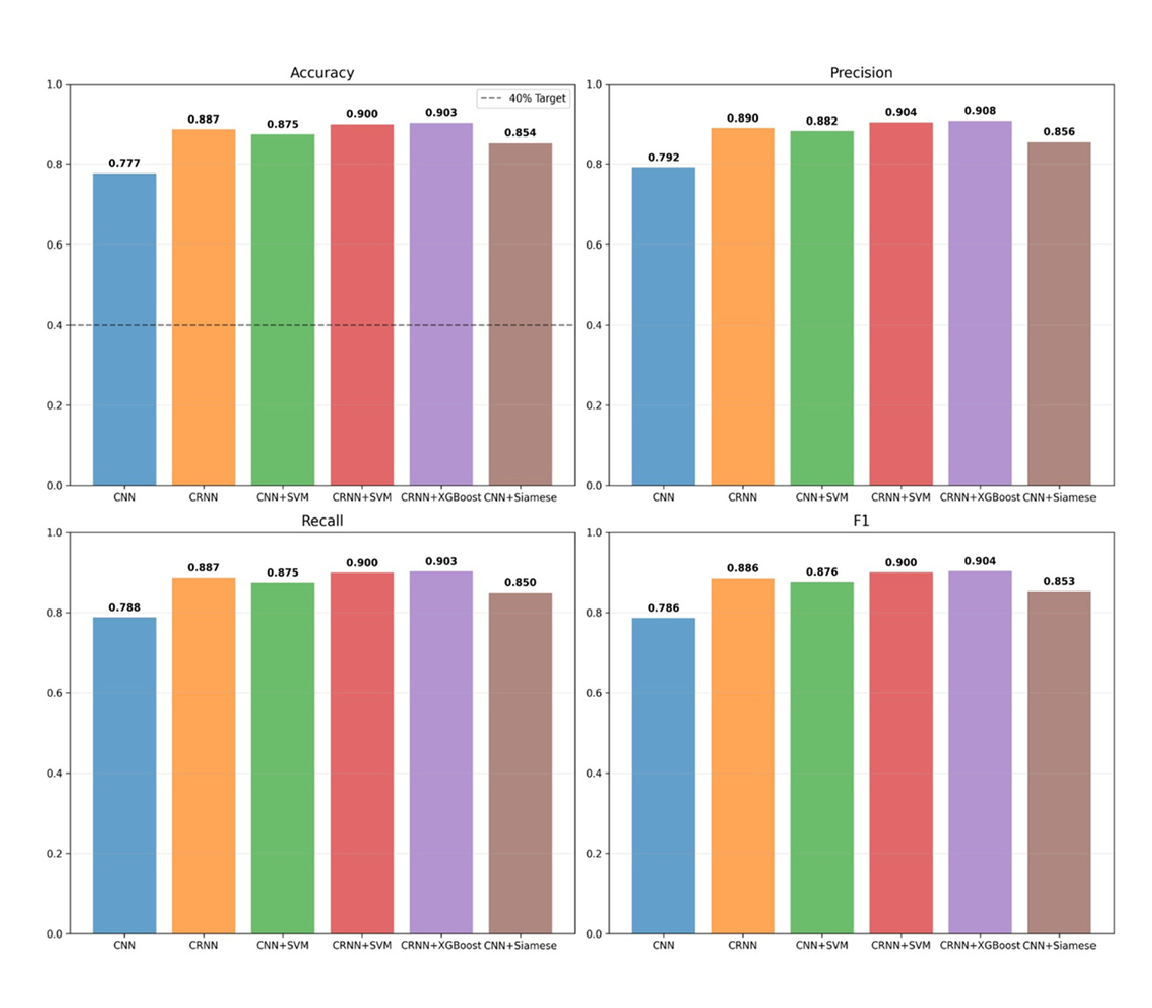
Extracts spatial stroke features and delivers ~77% writer accuracy as the baseline classifier.
CRNN
Stacks CNN and BiLSTM layers so the network learns shape, rhythm, and sequence; CTC loss supports fast transcription plus ~88% writer accuracy.
CNN + SVM
Feeds CNN embeddings into an SVM decision boundary, reaching ~87% accuracy and blending deep features with classical ML for smaller datasets.
CRNN + SVM
Supplies temporal CRNN features to an SVM classifier for 89.9% accuracy and improved robustness to writer-to-writer variation.
CRNN + XGBoost
Runs gradient-boosted trees on CRNN feature vectors, capturing complex interactions and delivering the best accuracy at 90.32%.
Siamese Network
Uses weight-sharing CNN twins with contrastive loss to decide whether two samples came from the same writer; ~85% verification accuracy adds a dedicated security layer.
Multi-Task Learning
Shared convolutional and recurrent layers learn both tasks simultaneously:
- CTC-based handwriting recognition.
- Style-driven writer classification.
This shared feature bank yields richer representations, better training efficiency, and workflows that mirror real forensic pipelines.
Optimization & Training Stability
The CRNN variants were run through staged learning-rate windows until convergence. Loss curves stayed smooth thanks to gradient clipping and CTC stabilization:
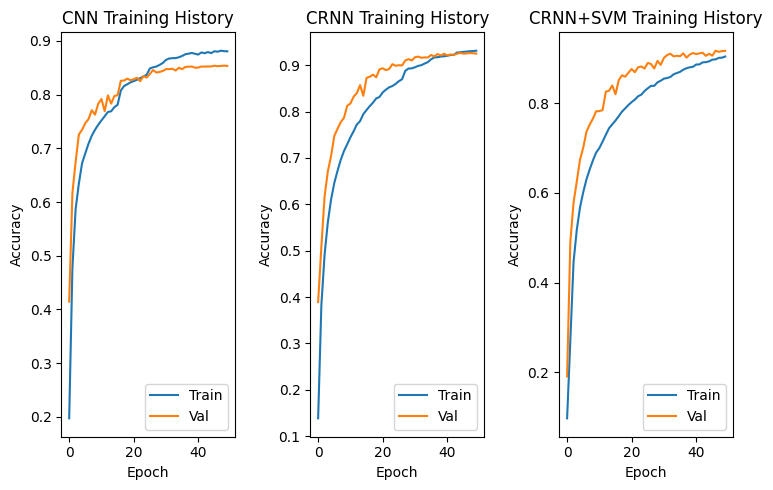
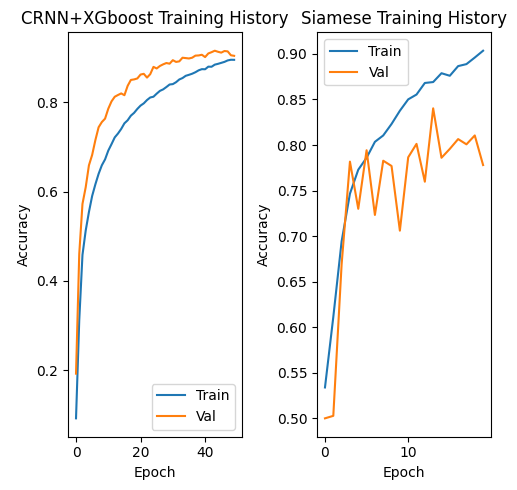
Performance Summary
| Model | Accuracy | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CNN | 77.70% | Strong spatial learner, limited temporal modeling |
| CRNN | 88.69% | Excellent sequence modeling |
| CNN + SVM | 87.46% | Deep features plus classical boundary |
| CRNN + SVM | 89.96% | Temporal features with SVM synergy |
| CRNN + XGBoost | 90.32% | Best overall performance |
| Siamese (verification) | 85.35% | Binary scoring for writer verification |
Each experiment ships with confusion matrices, per-writer metrics, and probability distribution charts.
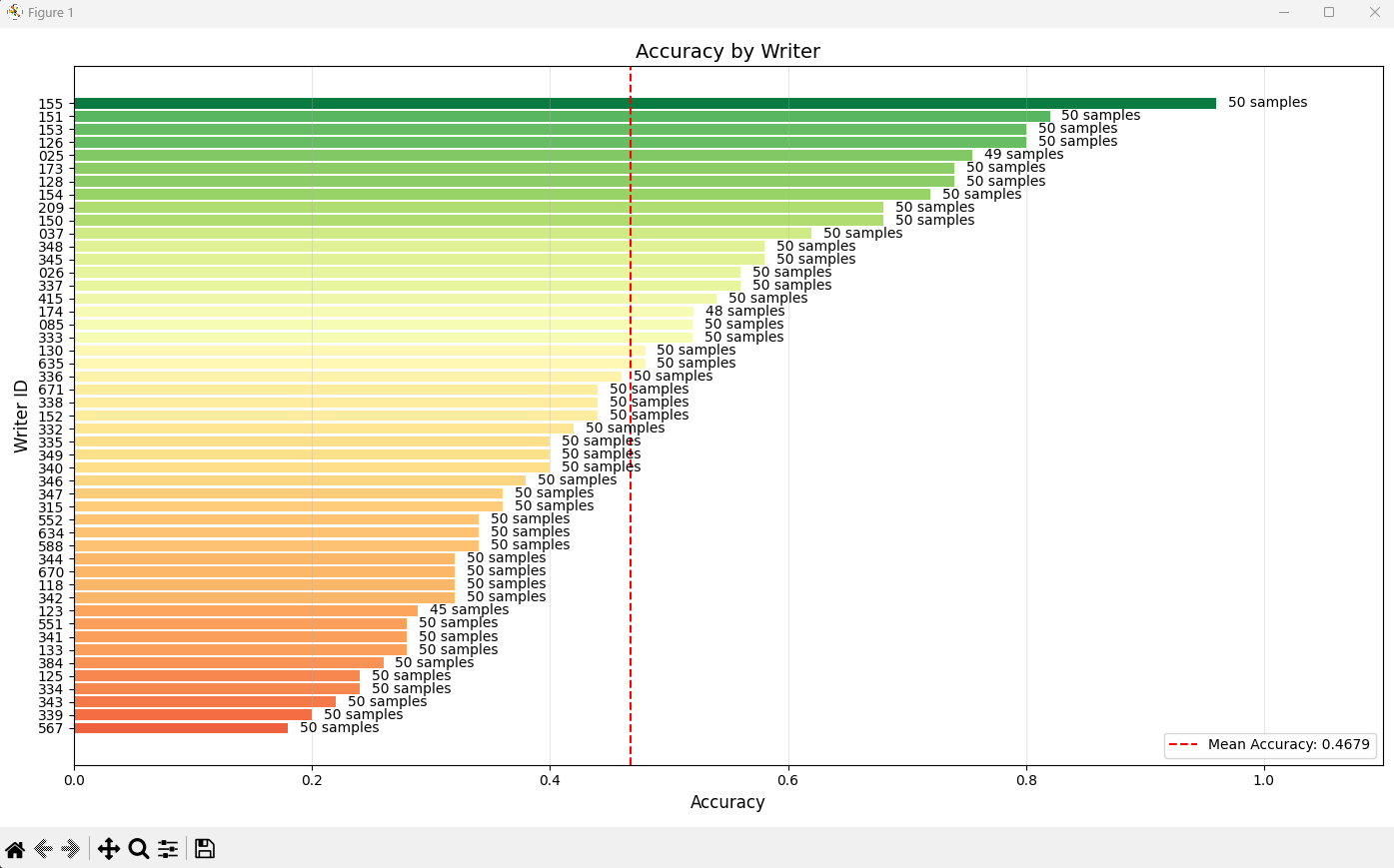
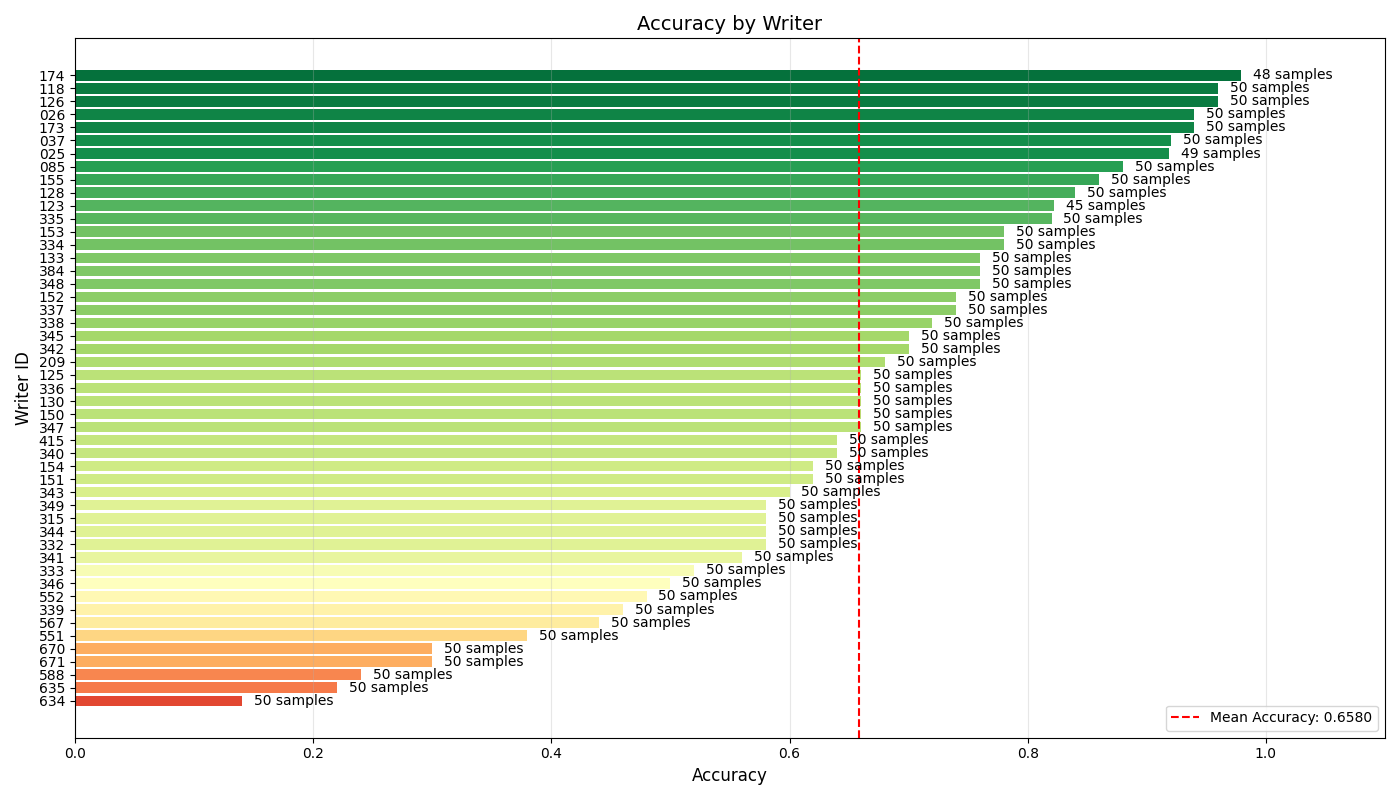
Strengths
- Comprehensive comparison of multiple architectures in a single pipeline.
- Fair evaluation via a balanced IAM subset.
- Strong hybrid performance from CRNN + XGBoost and CRNN + SVM.
- Siamese verification layer primes the system for biometric deployments.
- Visualizations and reporting tailored for forensic stakeholders (examples above).
Key Contributions
- Trained and compared six models (CNN, CRNN, hybrids, Siamese) under one infrastructure with uniform logging.
- Introduced a writer-ID approach that feeds CRNN features into XGBoost.
- Demonstrated dual-task learning where transcription and author ID share the same network.
- Published the balanced IAM subset pipeline for reproducibility.
Applications
- Forensic document reviews and signature/check verification.
- Biometric identity authentication systems.
- Archive automation and historical handwriting analytics.
- Intelligent handwriting analysis for banking or contract control.
Conclusion
The CRNN + XGBoost combo proves how deep sequential learning and ensemble decisions reinforce each other, while the Siamese verifier supplies the identity-check layer production systems expect. Overall the pipeline offers both scientific rigor and field readiness for handwriting-based biometrics.
Summary
I built an end-to-end AI pipeline that transcribes IAM handwriting with CTC while learning writer identity, elevates CRNN + XGBoost to peak accuracy, and layers on Siamese verification for additional security.