Overview
This project delivers a modular, biology-inspired robot snake featuring a five-servo body, Arduino-based control, HC-SR04 and DHT11 sensors, an ESP32-CAM stream, HC-06 Bluetooth connectivity, and an Android companion app. Together they form a remote-controlled platform that senses its surroundings while mimicking natural slithering.
Motivation
Snakes excel at squeezing through confined spaces, climbing uneven terrain, and maintaining balance without limbs. Replicating these capabilities enables search-and-rescue, pipeline inspection, surveillance, environmental monitoring, and education use cases via a portable, low-cost, modular platform.
Project Objectives
- Design a multi-segment body capable of realistic S-curve motion.
- Synchronize servos for forward/back/side movements via Bluetooth commands.
- Fuse ultrasonic distance, temperature/humidity, and camera data.
- Provide reliable wireless control through the HC-06 and a custom Android app.
- Surface sensor readings, video feeds, and emergency-stop controls in real time.
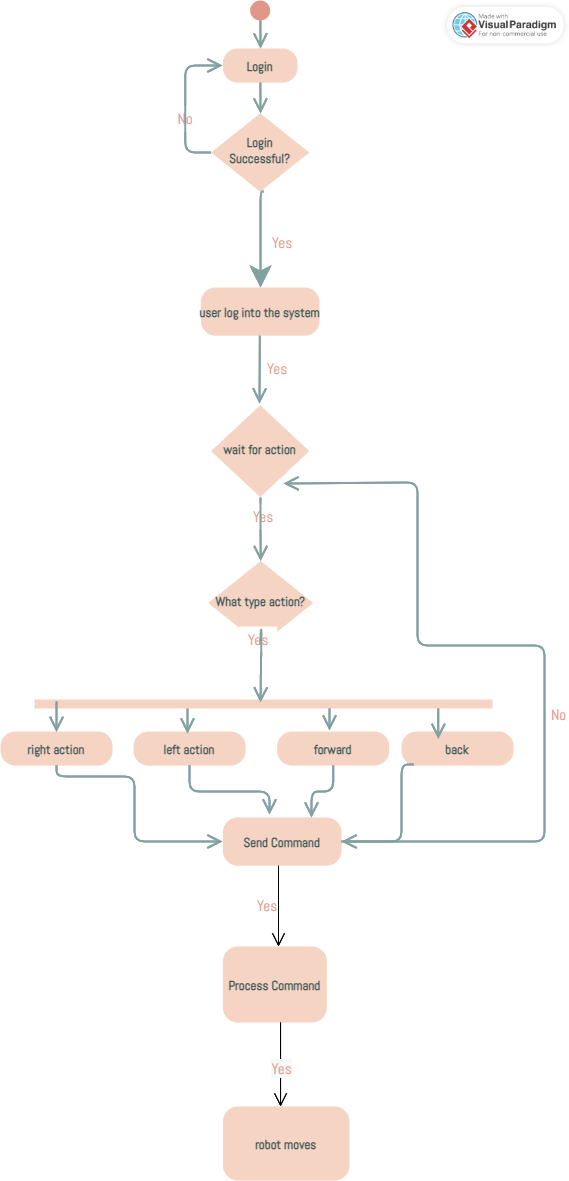
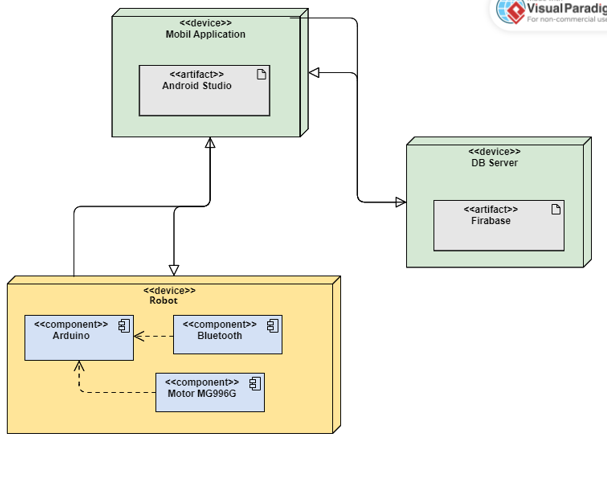
System Components & Architecture
- Servo Motors (×5): Provide bending and waveform locomotion along the spine.
- Arduino Uno: Drives PWM outputs, reads sensors, and orchestrates the control loop.
- HC-SR04: Mounted at the head for obstacle awareness.
- DHT11: Captures environmental temperature and humidity for the app.
- ESP32-CAM: Streams live video to give operators situational context.
- HC-06 Bluetooth: Delivers low-latency command and telemetry links to mobile devices.
- Power Management: Handles battery distribution, voltage regulation, and protection circuitry.
Software Architecture
Arduino Firmware
- Calculates PWM speed/angle profiles for all five servos.
- Processes HC-SR04 distances and triggers automatic stop/avoid maneuvers.
- Samples DHT11 data and injects it into Bluetooth packets.
- Coordinates ESP32-CAM plus HC-06 links with fail-safe handling.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#include <DHT.h>
#include <Servo.h>
#define trigPin 3
#define echoPin 2
#define DHTPIN 4
SoftwareSerial BTSerial(7, 6); // RX, TX
#define DHTTYPE DHT11
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
Servo s1, s2, s3, s4, s5;
long duration;
long distance;
int counter = 0;
float lag = 5.712;
float amplitude = 40;
float frequency = 1;
int offset = 6;
int delayTime = 1;
int startPause = 500;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
BTSerial.begin(9600);
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
s1.attach(8);
s2.attach(9);
s3.attach(10);
s4.attach(11);
s5.attach(12);
dht.begin();
delay(3000);
s1.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(5 * lag));
s2.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(4 * lag));
s3.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(3 * lag));
s4.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(2 * lag));
s5.write(90 + amplitude * cos(lag));
delay(startPause);
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
distance = (duration / 2) * 0.0343;
float temperature = dht.readTemperature();
float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
String dataString =
"Distance: " + String(distance) + " cm\n" +
"Temperature: " + String(temperature) + " degC\n" +
"Humidity: " + String(humidity) + "%\n";
Serial.println(dataString);
BTSerial.print(dataString);
delay(2000);
}// Send data via Bluetooth
BTSerial.print(dataString);
// Read from HC-06 for servo control
if (BTSerial.available()) {
int count = 0;
char receivedChar = BTSerial.read();
// Control servos based on received character
if (receivedChar == 'w') {
delay(startPause);
while (count < 5) {
moveForward();
count++;
}
count = 0;
} else if (receivedChar == 's') {
delay(startPause);
while (count < 5) {
moveBackward();
count++;
}
count = 0;
}
}
delay(2000); // Set measurement interval to 2 seconds
void moveForward() {
for (counter = 0; counter < 360; counter += 1) {
delay(delayTime);
s1.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + 5 * lag));
s2.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + 4 * lag));
s3.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + 3 * lag));
s4.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + 2 * lag));
s5.write(90 + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + lag));
}
}
void moveBackward() {
for (counter = 360; counter > 0; counter -= 1) {
delay(delayTime);
s1.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + 5 * lag));
s2.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + 4 * lag));
s3.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + 3 * lag));
s4.write(90 + offset + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + 2 * lag));
s5.write(90 + amplitude * cos(frequency * counter * PI / 180 + lag));
}
}Android Mobile App (Flutter/Java)
- Provides movement buttons (forward/back/left/right/camera tilt).
- Displays dashboards for sensor data and live video streams.
- Uses Firebase for authentication, preference storage, and logging.
- Maintains low-latency Bluetooth communication plus an emergency-stop control.
Backend / Firebase
- Manages user accounts and tokens.
- Stores preferences and session logs with secure access controls.
- Synchronizes real-time data with the mobile client.

Final field test showing the multi-servo locomotion, live video feed, and mobile control loop.
Functional Modules
- Locomotion: Generates S-curve movement via sinusoidal servo profiles with on-demand speed/direction changes.
- Obstacle Detection: Interprets ultrasonic readings to pause or warn the operator automatically.
- Environmental Monitoring: Continuously pushes DHT11 temperature/humidity updates.
- User Interface: Combines sensor, video, and control panels within a single screen.
- Wireless Communication: Uses encrypted HC-06 packets for responsive remote control.
SRS Highlights
- Functional: Authentication, real-time motion control, stable Bluetooth link, sensor telemetry, emergency stop.
- Non-Functional: Low-latency response, high connection reliability, intuitive UI, encrypted communication, modular codebase.
- Safety: Electrical/thermal protection, safe battery charging, rounded mechanical edges.
Results & Evaluation
- Locomotion: Delivers life-like slithering across narrow gaps and uneven surfaces.
- Sensor Accuracy: HC-SR04 detects obstacles with minimal false positives; DHT11 remains stable in lab conditions.
- Wireless Performance: Bluetooth connection stays persistent and responsive to commands.
- UI Experience: Android app streams sensor and video data smoothly while Firebase authentication remains uninterrupted.
Applications
- Search and rescue, hazardous inspection, and industrial pipeline monitoring.
- Environmental observation, military reconnaissance, and security.
- STEM education, biomimetic research, and swarm robotics experimentation.
Conclusion
By integrating hardware (servo chain, sensors, camera, power) with software (Arduino control algorithms, Bluetooth comms, Android UI, Firebase SRS), the robot snake delivers realistic motion, situational awareness, and remote control for nature-inspired robotics. Future iterations can expand into autonomous navigation, swarm coordination, or AI-driven decision-making.
Summary
I combined five servos, Arduino control, HC-SR04, DHT11, ESP32-CAM, HC-06 Bluetooth, and a Flutter-based mobile app to build a snake-inspired robot with S-curve locomotion and environmental awareness that is ready for scenarios ranging from rescue missions to education.